
GIS Termination: The 'Precision Interface' Connecting Cables to Gas-Insulated Switchgear
2025-10-09 15:59In the world of high-voltage power distribution, space is often at a premium, especially in dense urban areas or inside compact power substations. This is where Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS) shines—a system that encloses all essential components like circuit breakers and disconnectors in a sealed environment filled with insulating SF6 gas. But how do you connect a bulky, insulated power cable to this highly refined, sealed system? The answer lies in a critical component: the GIS Termination, a masterpiece of engineering that acts as a flawless "precision interface."
What is a GIS Termination?
A GIS Termination, also known as a GIS Cable End, is the specialized accessory mounted at the end of a power cable. Its primary function is to create a seamless, reliable, and fully insulated transition from the cable to the bushing of the GIS enclosure. It's not merely a seal; it's a complex interface that must manage electrical fields, different insulating mediums, and mechanical forces with absolute precision.
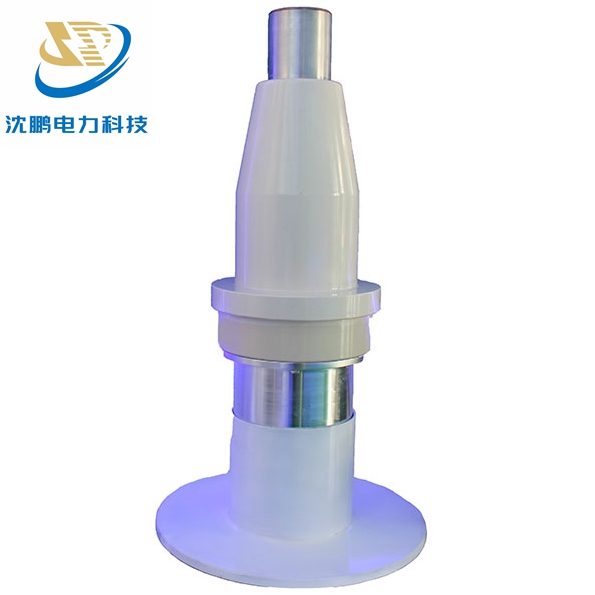
Key Characteristics: Bridging Two Worlds
The design of a GIS termination is dictated by its unique role as a bridge between the cable and the switchgear.
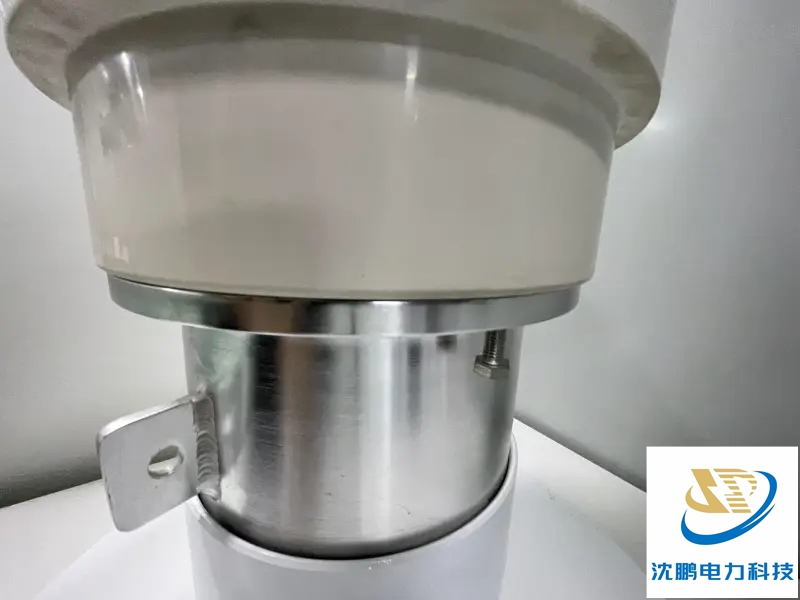

1. Transition of Insulating Media: The power cable uses solid insulation (like XLPE), while the GIS switchgear uses pressurized SF6 gas. The termination must perfectly manage the transition between these two different dielectric mediums, preventing any electrical field concentration that could lead to a breakdown.
2. Full Sealing Integrity: The termination forms a part of the GIS's sealed system. It must be absolutely leak-proof to maintain the integrity of the SF6 gas chamber, which is crucial for the switchgear's insulation and arc-quenching capabilities.
3. Compact and Integrated Design: Unlike outdoor terminations that are exposed to air, GIS terminations are designed to fit within the confined space of the GIS enclosure, requiring a highly compact and streamlined form factor.
The Plug-in Design: A Game of Millimeter Precision
Many modern GIS terminations feature a plug-in (or pluggable) design. This is a revolutionary feature that brings significant operational advantages, but it also demands the highest level of accuracy.
How it Works:
The termination assembly includes a male contact (often an epoxy resin insulator with an embedded electrode) that precisely aligns and plugs into a female socket connected to the GIS bushing. A specially designed jacking mechanism allows for smooth, controlled insertion and extraction.
The Advantages:
Ease of Installation and Maintenance: The plug-in design allows for the entire cable and termination to be installed or removed as a single unit. This dramatically simplifies maintenance, testing, or replacement procedures without requiring major disassembly of the GIS.
Excellent Contact Performance: The plug-in contact is engineered to provide a large surface area and high pressure, ensuring a low-resistance connection that can handle the rated current and short-circuit currents without overheating.
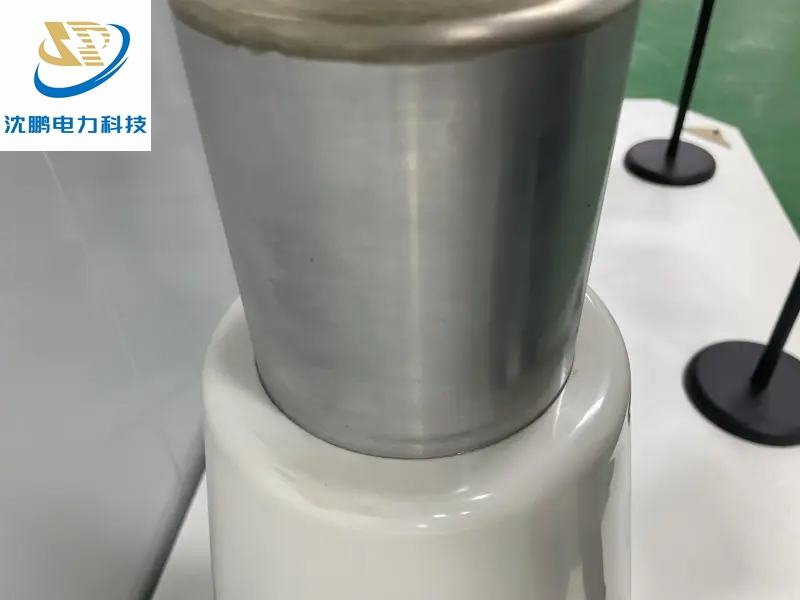

The Imperative of High Precision: Why Tolerances are Everything
The plug-in design and the high-voltage environment make precision non-negotiable. Every aspect of a GIS termination is a lesson in exactness:
Dimensional Accuracy: The mating surfaces, contact pins, and insulating components must be manufactured to micron-level tolerances. A misalignment of even a millimeter can prevent proper sealing, cause poor electrical contact, or damage the delicate components during insertion.
Perfect Interface Management: The electrical field at the cable-GIS interface is extremely high. The termination uses a stress control system—often a finely graded capacitive or geometric stress cone—that must be perfectly shaped and positioned to smoothly distribute the electrical stress and prevent dangerous partial discharges.
Impeccable Cleanliness: During assembly, the slightest particle of dust or moisture inside the termination or on the interface can create a focal point for electrical tracking, leading to eventual failure. Assembly is therefore performed in controlled, clean conditions.
The GIS termination is far more than a simple connector. It is a critical, high-precision component that ensures the integrity and performance of the entire Gas-Insulated Switchgear system. Its sophisticated plug-in design empowers utilities with unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in grid operation. However, this convenience is entirely dependent on its millimeter-perfect engineering and manufacturing. In the high-stakes environment of a modern power grid, the GIS termination stands as an unsung guardian, a "precision interface" quietly ensuring that power flows safely and reliably from the cable into the heart of the switchgear.
